Multimodal RAG with Gemini
 Pathway Team
Pathway Team
Multimodal RAG with Pathway and Gemini
The recent release of Google Gemini 1.5, with its impressive 1 million token context length window, has sparked discussions about the future of RAG. However, it hasn't rendered it obsolete. This system still offers unique advantages, especially in curating and optimizing the context provided to the model, ensuring relevance and accuracy. What is particularly interesting is how these advancements can be harnessed to enhance our projects and streamline our workflows.
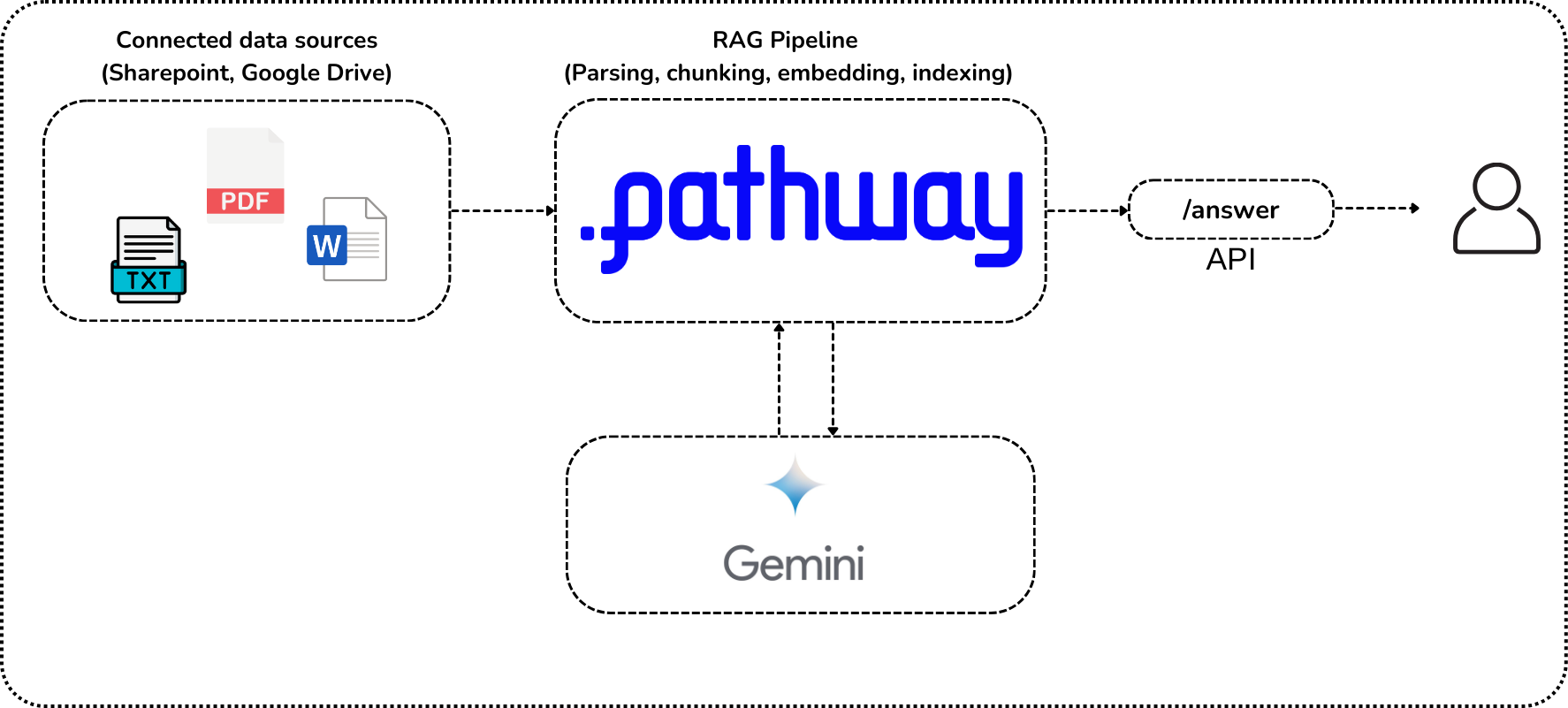
In this article, you'll learn how to set up a Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MM-RAG) system using Pathway and Google Gemini. You will walk through each step comprehensively, ensuring a solid understanding of both the theoretical and practical aspects of implementing Multimodal LLM and RAG applications.
You'll explore how to leverage the capabilities of Gemini 1.5 Flash and Pathway together. If you're interested in building RAG pipelines with OpenAI, we also have an article on Multimodal RAG using GPT-4o, which you can check out here.
If you want to skip the explanations, you can directly find the code here.
What this article will cover:
- What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
- Multimodality in LLMs
- Why is Multimodal RAG (MM-RAG) Needed?
- What is Multimodal RAG and Use Cases?
- Gemini Models
- Release of Gemini 1.5 and its impact on RAG architectures
- Comparing LlamaIndex and Pathway
- Hands-on Multimodal RAG with Google Gemini
Foundational Concepts
Why is Multimodal Rag needed?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances large language models by incorporating external knowledge sources before generating responses. This approach ensures relevant and accurate output. In today's data-rich world, documents often combine text and images to convey information comprehensively. However, most Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems overlook the valuable insights locked within images. As Multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) gain prominence, it's crucial to explore how we can leverage visual content alongside text in RAG, unlocking a deeper understanding of the information landscape.
Multimodal RAG is an advanced form of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that goes beyond text to incorporate various data types like images, charts, and tables. This expanded capability allows for a deeper understanding of complex information, leading to more accurate and informative outputs.
Two options for Multimodal RAG
- Multimodal Embeddings - The multimodal embeddings model generates vectors based on the input you provide, which can include a combination of image, text, and video data. The image embedding vector and text embedding vector are in the same semantic space with the same dimensionality. Consequently, these vectors can be used interchangeably for use cases like searching image by text, or searching video by image. Utilize multimodal embeddings to integrate text and images, retrieve relevant content through similarity search, and then provide both the raw image and text chunks to a multimodal LLM for answer synthesis.
- Text Embeddings - Generate text summaries of images using a multimodal LLM, embed and retrieve the text, and then pass the text chunks to the LLM for answer synthesis.
Comparing text-based and multimodal RAG
Multimodal RAG offers several advantages over text-based RAG:
- Enhanced knowledge access: Multimodal RAG can access and process both textual and visual information, providing a richer and more comprehensive knowledge base for the LLM.
- Improved reasoning capabilities: By incorporating visual cues, multimodal RAG can make better informed inferences across different types of data modalities.
Key Advantages of MM-RAG:
- Comprehensive Understanding: Processes multiple data formats for a better picture.
- Improved Performance: Visual data enhances efficiency in complex tasks.
- Versatile Applications: Useful in finance, healthcare, scientific research, and more.
Gemini Models
Gemini is Google's most capable and general AI model to date. Google has released several Gemini model variants, each tailored for different use cases and performance requirements.
Main Gemini Models:
- Gemini Ultra: The most powerful and advanced model, capable of handling complex tasks and offering state-of-the-art performance.
- Gemini Pro: A versatile model that balances performance and efficiency, suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Gemini Advanced: Designed for a broader set of tasks, offering a good balance of capabilities.
- Gemini Lite: A smaller, more efficient model focused on speed and responsiveness, ideal for resource-constrained environments.
Additional Variants:
- Gemini 1.5 Flash: Optimized for high-volume, cost-effective applications.
- Gemini 1.5 Pro: Offers a balance of performance and capabilities.
- Gemini 1.0 Pro Vision: Includes vision capabilities for processing images and videos.
- Gemini 1.0 Pro: Text-based model for general language tasks.
Benefits of Building with Gemini:
Free Credits: Google Cloud offers new users up to $300 in free credits. This can be used to experiment with Gemini models and other Google Cloud services. You can also seamlessly integrate MM-RAG applications with Google's Vertex AI platform for streamlined machine learning workflows.
Release of Gemini 1.5 and its impact on RAG architectures
The Gemini 1.5 Flash model, released on May 24, 2024, revolutionized AI with its enhanced speed, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, long context window, and multimodal reasoning capabilities.
Did Google Gemini 1.5 Kill the need of RAG?
In one word “No”. Gemini 1.5, with a 1M context length window, has sparked a new debate about whether RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) is still relevant or not. LLMs commonly struggle with hallucination. To address this challenge, two solutions were introduced, one involving an increased context window and the other utilizing RAG. Gemini 1.5 outperforms Claude 2.1 and GPT-4 Turbo as it can assimilate entire code bases, process over 100 papers, and various documents, but it surely hasn’t killed RAG.
RAG leverages your private knowledge database for effective Q&A while ensuring the security of sensitive information like trade secrets, confidential IP, GDPR-protected data, and internal documents. For more detailed insights explore our article on Private RAG with Connected Data Sources using Mistral, Ollama, and Pathway here.
Additionally in traditional RAG pipelines, you can enhance performance by tweaking the retrieval process, changing the embedding model, adjusting chunking strategies, or improving source data. However, with a "stuff-the-context-window-1M-tokens" strategy, your only option is to improve the source data since all data is given to the model within the token limit. Additionally the context window may be filled with many relevant facts, but 40% or more of them are “lost” to the model. If you want to make sure the model is actually using the context you are sending it, you are best off curating it first and only sending the most relevant context. In other words, doing traditional RAG.
Here in this template you will use the Gemini 1.5 Flash but you can also use other multimodal models by gemini accordingly.
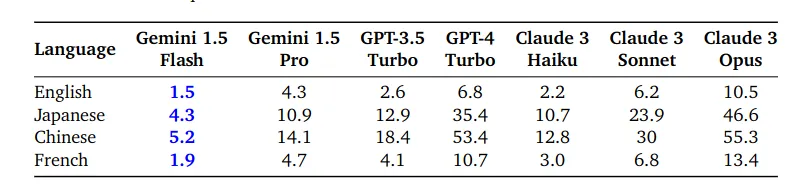
Multimodality with Gemini-1.5-Flash
Gemini 1.5 Flash is the newest addition to the Gemini family of large language models, and it’s specifically designed to be fast, efficient, and cost-effective for high-volume tasks. This is achieved by being a lighter model than the Gemini 1.5 Pro.
According to the paper from Google DeepMind, Gemini 1.5 Flash is “a more lightweight variant designed for efficiency with minimal regression in quality” and uses the transformer decoder model architecture “and multimodal capabilities as Gemini 1.5 Pro, designed for efficient utilization of tensor processing units (TPUs) with lower latency for model serving.”
Gemini 1.5 Flash: Key Features
- Speed and Efficiency: Fastest Gemini model at 60 tokens/second, ideal for real-time tasks, reducing costs by delaying autoscaling.
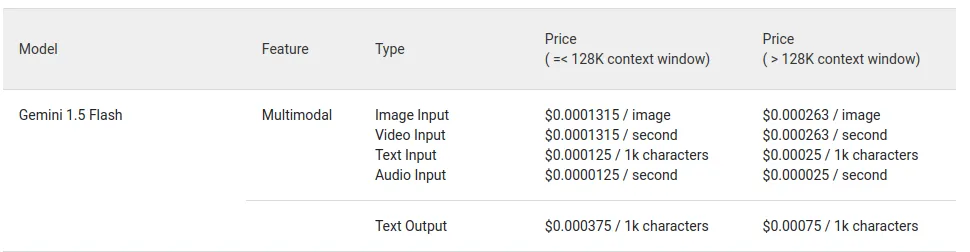
- Cost-Effective: 1/10 the price of Gemini 1.5 Pro and cheaper than GPT-3.5.
- Long Context Window: Processes up to one million tokens, handling one hour of video, 11 hours of audio, or 700,000 words without losing accuracy.
- Multimodal Reasoning: Understands text, images, audio, video, PDFs, and tables. Supports function calling and real-time data access.
- Great Performance: High performance with large context windows, excelling in long-document QA, long-video QA, and long-context ASR.
Hands on Multimodal RAG with Google Gemini
Step 1: Installation
First, we need to install the required packages: pathwayall, litellm==1.40.0 and google-generativeai.
!pip install 'pathway[all]>=0.14.0' litellm==1.40.0
Step 2: Imports and Environment Setup
Next, we import the necessary libraries and set up the environment variables.
import logging
import os
import google.generativeai as genai
import litellm
import pathway as pw
from pathway.udfs import DiskCache, ExponentialBackoffRetryStrategy
from pathway.xpacks.llm import embedders, llms, parsers, prompts, splitters
from pathway.xpacks.llm.question_answering import BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer
from pathway.xpacks.llm.vector_store import VectorStoreServer
# Set the logging level for LiteLLM to DEBUG
os.environ["LITELLM_LOG"] = "DEBUG" # to help in debugging
Step 3: API Key Setup and License Key Setup
Set up the API key and the Pathway license key:
# Api key setup
GEMINI_API_KEY = "Paste your Gemini API Key here"
os.environ["GEMINI_API_KEY"] = GEMINI_API_KEY
os.environ["TESSDATA_PREFIX"] = "/usr/share/tesseract/tessdata/"
genai.configure(api_key=GEMINI_API_KEY)
# License key setup
pw.set_license_key("demo-license-key-with-telemetry")
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s"
)
Step 4: Upload your file
Create a ./data directory if it doesn't already exist. This is where the uploaded files will be stored. Then upload your pdf documents.
You can also omit this cell if you are running locally on your system - in that case create a data folder in the current directory and copy the files and comment out this cell.
!mkdir -p data
# Demo pdf for testing
!wget -q -P ./data/ https://github.com/pathwaycom/llm-app/raw/main/templates/multimodal_rag/data/20230203_alphabet_10K.pdf
Reading PDF Data
Next, we read the PDF data from a folder.
# Read the PDF data
folder = pw.io.fs.read(
path="./data/",
format="binary",
with_metadata=True,
)
sources = [folder] # you can add any other Pathway connector here!
Step 5: Document Processing and Question Answering Setup
Setting Up LiteLLM Chat
Set up a LiteLLM chat instance with retry and cache strategies:
# Setup LiteLLM chat
chat = llms.LiteLLMChat(
model="gemini/gemini-1.5-flash", # Model specified for LiteLLM
retry_strategy=ExponentialBackoffRetryStrategy(max_retries=6, backoff_factor=2.5),
temperature=0.0,
)
Setting Up Embedder
Let's utilize Gemini embedders. The GeminiEmbedder class in Pathway provides an interface for interacting with Gemini embedders. It generates semantic embeddings with a specified model, providing methods for single items (embed), batches (embed_batch), and direct calls.
# Setup embedder
embedder = embedders.GeminiEmbedder(
model="models/embedding-001",
retry_strategy=ExponentialBackoffRetryStrategy(max_retries=6, backoff_factor=2.5),
) # Specify embedder here
Setting Up Parser
Next, we set up a parser for the document store.
# Setup parser
table_args = {
"parsing_algorithm": "llm", # for tables
"llm": chat,
"prompt": prompts.DEFAULT_MD_TABLE_PARSE_PROMPT,
}
image_args = {
"parsing_algorithm": "llm", # for images
"llm": chat,
"prompt": prompts.DEFAULT_IMAGE_PARSE_PROMPT,
}
parser = parsers.DoclingParser(multimodal_llm=chat)
Setting Up Document Store
We will set up the document store with the sources, embedder, and parser.
# Setup document store
# splitter = splitters.TokenCountSplitter()
doc_store = VectorStoreServer(
*sources,
embedder=embedder,
splitter=splitter,
parser=parser,
)
Step 6: Setting Up Question Answerer Application
We will set up the question answerer application using the LiteLLM-based chat object.
# Setup question answerer application
app = BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer(
llm=chat, # Using the LiteLLM-based chat object
indexer=doc_store, search_topk=2,
short_prompt_template=prompts.prompt_qa)
Building and Running the Server
Finally, we build and run the server.
# Build and run the server
app_host = "0.0.0.0"
app_port = 8000
app.build_server(host=app_host, port=app_port)
import threading
t = threading.Thread(target=app.run_server, name="BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer")
t.daemon = True
thr = t.start()
from pathway.xpacks.llm.question_answering import RAGClient
# Initialize the RAG client
client = RAGClient(host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
# Example usage
response = client.answer("What is the Total Stockholders' equity as of December 31, 2022?")
print(response)
$256,144 million
Now your chatbot is now running live! You can ask any questions and get information from your documents instantly.
Conclusion
This article demonstrated how to implement a Multimodal RAG service using Pathway and Gemini. The setup leverages the capabilities of LiteLLM to process and query multimodal data effectively. If you're looking for a cost-effective alternative, consider using the Gemini Mini, which provides great performance at a lower cost.
For more detailed insights and an alternative approach, check out our article on multimodal RAG using GPT-4o here. This will give you another perspective on how to handle multimodal RAG applications using different models and techniques. By following the steps outlined above, you can efficiently integrate and utilize various data types to enhance your AI applications, ensuring more accurate and contextually rich outputs.

Pathway Team