Adaptive RAG App
 Pathway Team
Pathway Team
Deploy with GCP |
Deploy with AWS |
Deploy with Azure |
![]() Deploy with Render
Deploy with Render
End to end Adaptive RAG with Pathway
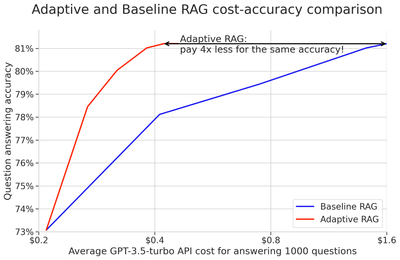
This is the accompanying code for deploying the adaptive RAG technique with Pathway. To understand the technique and learn how it can save tokens without sacrificing accuracy, read our showcase.
To learn more about building & deploying RAG applications with Pathway, including containerization, refer to demo question answering.
Introduction
This app relies on modules provided under pathway.xpacks.llm.
BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer is the base class to build RAG applications with Pathway vector store and Pathway xpack components.
It is meant to get you started with your RAG application right away.
Here, we extend the BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer to implement the adaptive retrieval and reply to requests in the endpoint /v2/answer.
Since we are interested in changing the behavior and logic of the RAG, we only modify answer function that handles all this logic, and then replies to the post request.
answer function takes the pw_ai_queries table as the input, this table contains the prompt, and other arguments coming from the post request, see the BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer class and defined schemas to learn more about getting inputs with post requests.
We use the data in this table to call our adaptive retrieval logic.
To do that, we use answer_with_geometric_rag_strategy_from_index implementation provided under the pathway.xpacks.llm.question_answering.
This function takes an index, LLM, prompt and adaptive parameters such as the starting number of documents. Then, iteratively asks the question to the LLM with an increasing number of context documents retrieved from the index.
We encourage you to check the implementation of answer_with_geometric_rag_strategy_from_index.
Customizing the pipeline
The code can be modified by changing the app.yaml configuration file. To read more about YAML files used in Pathway templates, read our guide.
In the app.yaml file we define:
- input connectors
- LLM
- embedder
- index and any of these can be replaced or, if no longer needed, removed. For components that can be used check Pathway LLM xpack, or you can implement your own.
You can also check our other templates - Question Answering RAG, Multimodal RAG or Private RAG. As all of these only differ in the YAML configuration file, you can also use them as an inspiration for your custom pipeline.
Here some examples of what can be modified.
LLM Model
You can choose any of the models offered by Open AI, like GPT-5, GPT-4.1, or GPT-4o. You can find the whole list on their models page.
You simply need to change the model to the one you want to use, e.g., to use GPT-5:
$llm: !pw.xpacks.llm.llms.OpenAIChat
model: "gpt-5"
retry_strategy: !pw.udfs.ExponentialBackoffRetryStrategy
max_retries: 6
cache_strategy: !pw.udfs.DefaultCache
capacity: 8
The default model is gpt-4.1-mini.
You can also use different provider, by using different class from Pathway LLM xpack, e.g. here is configuration for locally run Mistral model.
$llm: !pw.xpacks.llm.llms.LiteLLMChat
model: "ollama/mistral"
retry_strategy: !pw.udfs.ExponentialBackoffRetryStrategy
max_retries: 6
cache_strategy: !pw.udfs.DiskCache
temperature: 0
top_p: 1
api_base: "http://localhost:11434"
Webserver
You can configure the host and the port of the webserver. Here is the default configuration:
host: "0.0.0.0"
port: 8000
Cache
You can configure whether you want to enable cache or persistence, to avoid repeated API accesses, and where the cache is stored. Default values:
persistence_mode: !pw.PersistenceMode.UDF_CACHING
persistence_backend: !pw.persistence.Backend.filesystem
path: ".Cache"
Data sources
You can configure the data sources by changing $sources in app.yaml.
You can add as many data sources as you want. You can have several sources of the same kind, for instance, several local sources from different folders.
The sections below describe how to configure local, Google Drive and Sharepoint source, and you can check the examples of YAML configuration in our user guide. While these are not described in this Section, you can also use any input connector from Pathway package.
By default, the app uses a local data source to read documents from the data folder.
Local Data Source
The local data source is configured by using map with tag !pw.io.fs.read. Then set path to denote the path to a folder with files to be indexed.
Google Drive Data Source
The Google Drive data source is enabled by using map with tag !pw.io.gdrive.read. The map must contain two main parameters:
object_id, containing the ID of the folder that needs to be indexed. It can be found from the URL in the web interface, where it's the last part of the address. For example, the publicly available demo folder in Google Drive has the URLhttps://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1cULDv2OaViJBmOfG5WB0oWcgayNrGtVs. Consequently, the last part of this address is1cULDv2OaViJBmOfG5WB0oWcgayNrGtVs, hence this is theobject_idyou would need to specify.service_user_credentials_file, containing the path to the credentials files for the Google service account. To get more details on setting up the service account and getting credentials, you can also refer to this tutorial.
Besides, to speed up the indexing process you may want to specify the refresh_interval parameter, denoted by an integer number of seconds. It corresponds to the frequency between two sequential folder scans. If unset, it defaults to 30 seconds.
For the full list of the available parameters, please refer to the Google Drive connector documentation.
SharePoint Data Source
This data source requires Scale or Enterprise license key - you can obtain free Scale key on Pathway website.
To use it, set the map tag to be !pw.xpacks.connectors.sharepoint.read, and then provide values of url, tenant, client_id, cert_path, thumbprint and root_path. To read about the meaning of these arguments, check the Sharepoint connector documentation.
Running the app
To run the app, depending on the configuration, you may need to set up environmntal variables with LLM provider keys. By default, this template uses OpenAI API, so to run it you need to set OPENAI_API_KEY environmental key or create an .env file in this directory with your key: OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-.... If you modify the code to use another LLM provider, you may need to set a relevant API key.
With Docker
In order to let the pipeline get updated with each change in local files, you need to mount the folder onto the docker. The following commands show how to do that.
# Build the image in this folder
docker build -t adaptiverag .
# Run the image, mount the `data` folder into image
# -e is used to pass value of OPENAI_API_KEY environmental variable
docker run -v ./data:/app/data -e OPENAI_API_KEY -p 8000:8000 adaptiverag
Locally
To run locally you need to install the Pathway app with LLM dependencies using:
pip install pathway[all]
Then change your directory in the terminal to this folder and run the app:
python app.py
Using the app
Finally, query the application with;
curl -X 'POST' 'http://0.0.0.0:8000/v2/answer' -H 'accept: */*' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{
"prompt": "What is the start date of the contract?"
}'
{"response": "December 21, 2015 [6]"}

Pathway Team